Dana Norwood is a second-year dual degree candidate in the MS/MPH program at the Tufts Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy and the Tufts School of Medicine. Combined with an academic background in Biology and Social Justice, her academic focus lies in the intersection of nutrition equity, access, and effective communication strategies.
Dana has actively contributed to the Tufts Food and Nutrition Innovation Institute, where she has told the inspiring stories of health-forward food entrepreneurs of color, highlighting their impact on community health. Passionate about nutrition equity, she is dedicated to developing and implementing innovative interventions that empowers healthy eating behaviors across diverse populations.
Final Presentation
Final Project
- PROJECT DESCRIPTION
Exploring Ethical Implications of AI Use in Personalized Nutrition
With the help of machine learning, a sub-branch of artificial intelligence, there is a growing desire to leverage its predictive modeling power to aid precision nutrition research (Kirk, 2021). This observational study aims to examine the ethical implications of the use of AI in personalized nutrition programs, with a focus on the impact of these technologies on individuals’ privacy concerns, trust in institutions, and equitable health outcomes. Through a detailed analysis of both positive and negative ethical implications, this study aims to contribute to the broader discussion of ethical AI implementation in personalized nutrition.
Research Question
This observational study answers the question: “How does the implementation of AI-driven personalized nutrition programs impact individuals’ privacy concerns, trust in institutions, and equitable health outcomes?” This question denotes two driving arcs—enhancing personalized health outcomes while safeguarding ethical standards and promoting equitable access.
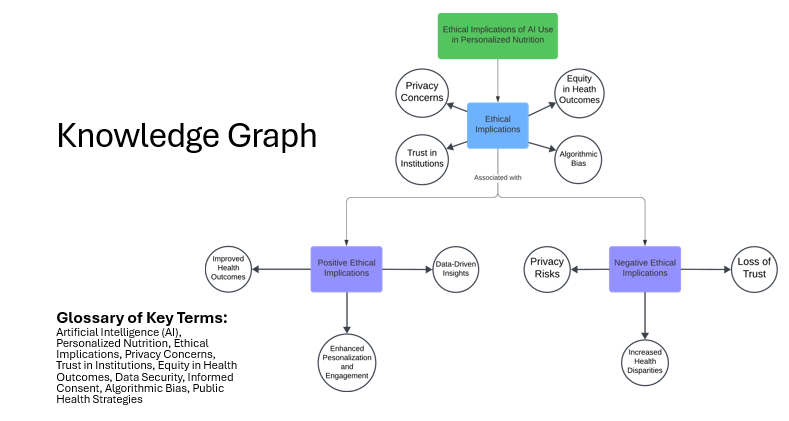
Positive Ethical Implications
Improved Health Outcomes: One of the foremost positive implications of AI in personalized nutrition is the potential for significantly improved health outcomes. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to provide tailored dietary recommendations that align with individual health profiles, genetic predispositions, and lifestyle factors. This precision can lead to more effective nutritional interventions, aiming to reduce the risk of chronic diseases while enhancing overall well-being.
Enhanced Personalization and Engagement: AI facilitates a higher degree of personalization in dietary recommendations, fostering greater user engagement and adherence. Personalized nutrition plans that consider an individual’s unique biological, lifestyle, and cultural contexts are more likely to be followed, leading to sustained health improvements and better quality of life.
Data-Driven Insights: AI’s capability to process and analyze large datasets can generate valuable insights into population health trends, dietary behaviors, and the effectiveness of various nutritional interventions. These insights can inform public health strategies, contributing to broader societal benefits.
Negative Ethical Implications
Privacy Concerns: The use of AI in personalized nutrition requires the collection and analysis of expansive personal health data, raising important privacy concerns. Individuals may feel uneasy about the potential misuse of their data, unauthorized access, or data breaches. Ensuring robust data security measures and transparent data handling practices is critical to mitigating their concerns.
Algorithmic Bias and Health Disparities: AI algorithms are only as good as the data they are trained on. Biases in training data can lead to algorithmic bias, resulting in unequal treatment and recommendations that may disproportionately favor certain demographics over others. This can exacerbate existing health disparities and undermine the equity of personalized nutrition programs.
Erosion of Trust in Institutions: Privacy concerns and instances of data misuse can erode trust in the institutions responsible for implementing AI-driven personalized nutrition programs. Without trust, individuals are less likely to engage with these technologies, limiting their potential benefits. Building and maintaining trust through transparent practices and robust ethical guidelines is essential.
Equity in Health Outcomes: Ensuring equitable access to AI-driven personalized nutrition is a significant ethical challenge. There is a risk that these technologies could widen health disparities if access is limited to certain socioeconomic groups. It is crucial to design and implement these programs in ways that ensure broad and equitable access to all population segments.
Conceptual Framework
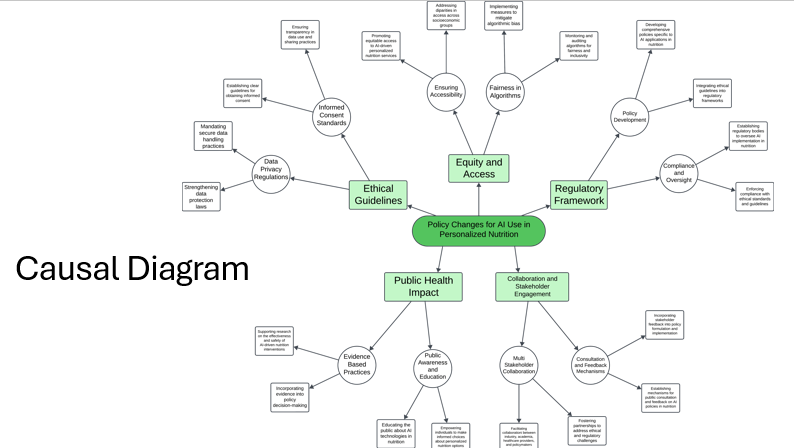
A knowledge graph has been developed to illustrate the ethical implications of AI use in personalized nutrition. Branching out from this central node are key positive and negative ethical implications. Going deeper, a causal diagram denoting the possible impacts of policy changes was also created. These visual representations aid in understanding the complex connections between factors and the overarching ethical considerations therein.
Conclusion
The integration of AI into personalized nutrition holds immense promise for improving health outcomes and enhancing the personalization of dietary recommendations. However, it also brings forth important ethical challenges that must be addressed to ensure equitable and trustworthy implementation. By exploring both the positive and negative ethical implications, this study aims to contribute to the development of ethically responsible AI practices in personalized nutrition. Ultimately, the goal is to utilize the benefits of AI while ensuring ethical standards and promoting equity, thereby maximizing the potential for positive health impacts on individuals and society.
Given the preliminary nature of this observational study and its conclusions, further exploration and discussion on the ethical implications of AI in personalized nutrition is necessary and warmly invited. Leveraging innovation and ethics is key to successful integration into the precision nutrition space.