![[describe image in words]](http://media.npr.org/assets/img/2017/02/01/title_ep01_wide-05ac79a0ebeb8ee9ba826864096789cdbf78b5c4-s400-c85.jpg) Xaver Xylophon for NPR
Xaver Xylophon for NPR
Our first germs didn’t do much damage, until we gave up our hunter-gatherer ways and started farming. Watch Episode 1 of a three-part animated miniseries on the battle between humans and germs.
Watch the video NPR.org
 EURAC/Marion Lafogler
EURAC/Marion Lafogler
Scientists analyzed the tummy of a 5,300-year-old ice mummy and found bacteria that many modern humans still carry. The results, published in the journal Science, suggest that the community of microbes living on and in humans has existed for millennia.
Read more at NPR.org.
 Satoshi Omura, Youyou Tu and William C. Campbell share in the 2015 Nobel Prize in Medicine
Satoshi Omura, Youyou Tu and William C. Campbell share in the 2015 Nobel Prize in Medicine
Nobel Prize Committee
The medicines they helped develop are credited with improving the lives of millions. Among the three winners: William C. Campbell of Drew University, for his work on the roundworm parasite.
Read more at NPR.org.
 Cellou Binani/AFP/Getty Images
Cellou Binani/AFP/Getty Images
In a small trial, an experimental vaccine protected 100 percent of people at high risk for Ebola. But more data are needed to figure out exactly how well the vaccine works. The study was published last week in the journal The Lancet.
Read more at NPR.org.
 Sean Hawkey
Sean Hawkey
The trial of the VSV-EBOV vaccine was called Ebola ça Suffit — French for “Ebola that’s enough.” Researchers say it’s both effective and quick, with no new Ebola cases 6 days after vaccination. The findings were published in The Lancet medical journal on Friday.
Read more at NPR.org.
 Rotary International
Rotary International
Health officials in Nigeria are celebrating an impressive milestone: The country has gone one year without a single case of polio. The world is now one step closer to making polio the second human infectious disease – after smallpox – to be eradicated with an effective vaccination campaign.
Read more at iflscience.com.
 AMISOM via Flickr
AMISOM via Flickr
The world’s first malaria vaccine has just passed an important hurdle. The vaccine, which researchers have been working on for 30 years, has been given a green light by European regulators.
Read more at iflscience.com.
 Ed Jones/AFP/Getty Images
Ed Jones/AFP/Getty Images
When Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) erupted in South Korea, people started wearing masks everywhere, even at weddings. So how good are these masks at stopping MERS or even the flu?
Read more at NPR.org.
 Courtesy of Kathy Wolfe
Courtesy of Kathy Wolfe
When 17-year-old Raymond Wang read about how easily some diseases spread on planes, he thought airlines could do better. So he went to work — and won $75,000 at the International Science Fair.
Read more at NPR.org.
 Michael Duff/AP
Michael Duff/AP
Over the past few months, case tallies have dipped toward zero, only to bounce back up. Health officials worry the outbreak could never end if people keep hiding cases and dead bodies.
Read more at NPR.org.
 Science Source
Science Source
A woman who caught pneumonic plague in Colorado last summer likely contracted it from her friend or his dog. Antibiotics limited the outbreak to four people and cured them.
Read more at NPR.org.
It’s a deadly combination of infection and inflammation striking more than a million Americans every year. Doctors can treat the symptoms of sepsis, but they still can’t treat the underlying problem.
Read more at NPR.org.
 Ira Gay Sealy/Denver Post via Getty Images
Ira Gay Sealy/Denver Post via Getty Images
It took 15 years and 250 million vaccines, but this week, health authorities officially declared North America and South America free of rubella — a virus that can cause severe birth defects.
Read more at NPR.org.
 Photofusion/UIG via Getty Images
Photofusion/UIG via Getty Images
When the U.S. introduced the measles vaccine, childhood deaths from all infections plummeted. Scientists think they might know why: Benefits of the measles vaccine go way beyond the measles.
Read more at NPR.org.
 CDC/Science Source
CDC/Science Source
Travelers are bringing a nasty bacterial disease to the U.S. and spreading it to others. The bacteria cause bad diarrhea and are touch to treat because they’re resistant to the top antibiotic.
Read more at NPR.org.
 Obadia et al/PLOS Computational Biology
Obadia et al/PLOS Computational Biology
Over four months of tracking and testing, French researchers mapped the hops that bacteria made from one person to another. Within a month, a third of patients were newly colonized with staph.
Read more at NPR.org.
 Credit: George Frey/Landov
Credit: George Frey/Landov
The quick rise of measles infections in the wake of cases reported among Disneyland visitors underscores how even a small dip in vaccination rates can allow the virus to spread.
Read more at NPR.org.

A new study suggests that Swedish kids growing up in families that wash their dishes by hand are less likely to develop certain allergies than those families with dishwashers. These findings are the latest support to the “hygiene hypothesis” that proposes a lack of childhood exposure to infectious agents and parasites increases susceptibility to allergic diseases by suppressing the natural development of the immune system. But there may be more to it…
Read more at NPR.org.

A measles outbreak linked to Disneyland has nearly doubled in size since last week with 45 reported cases in California and seven more illnesses confirmed in at least three other states and Mexico. A contagious disease expert contends that the recent spread of measles is being fueled by a portion of parents who refused to vaccinate their children — an estimated one in 10 people today is perhaps susceptible to the virus.
Measles is very infectious because it spreads through the air, so you can catch it by standing next to someone who is infected. Initial measles symptoms include fever, cough, running nose and red eyes. After a few days, a red rash appears on the face and then spreads downward to the rest of the body. Measles can be serious and even fatal for small children.
Read more at NBCNews.com.

One of the most important medical advances may also be the simplest: hand-washing. It’s the best defense against spreading disease. And its power was discovered long before anyone knew about germs.
Read more about the history of hand-washing at NPR.org.

Ebola viruses (in blue) leaving an infected cell (in yellow). Image by the NIAID.
This PBS article contains detailed information on the Ebola path of transmission from person-to-person. It also describes in depth the mechanisms by which it causes damage to the host.

A drawing of the Ebola virion.
Since the Ebola outbreak spread from Africa to other continents, many people have expressed concerns that it may mutate and gain the ability to go airborne (stay active in the air for long enough to travel and be spread to other people). But how likely is that to happen? This article in the NYT shares the professional opinions of virologists on the virus evolution, properties, and their thoughts on the probability of the occurrence of such a major shift.
The U.S. has now reported the first Ebola case diagnosed in the country. The patient arrived in Dallas from Liberia a few weeks ago. Read more about the case on the NPR website. Authorities are certain they will be able to control the spread of the diseases. Ebola is not airborne which means that the virus cannot survive in a free form in the air so it is not easily spread from person to person. However, this case reminds us of how connected we are and how any deadly infectious disease outbreak no matter how distant from our living place matters now even more than ever since infectious diseases do not recognize international borders.

An electron micrograph of the Ebola virus.

The New England Journal of Medicine has published an interactive graphic to track the current Ebola outbreak in West Africa. The map contains information on past outbreaks too as well as basic description of the disease, how it spreads, etc. You can view the graphic on the NEJM website.

Smallpox virions (electron microscopy image). Source
Smallpox is the only human infectious disease which was eradicated from planet Earth. The success was the result of a massive worldwide vaccination campaign that finished successfully in the late 1970s of the twentieth century. But USA and Russia kept live samples of the virus. Later this month the WHO will discuss again whether to keep or destroy the samples.
Should We Destroy Our Last Living Samples of the Virus That Causes Smallpox?
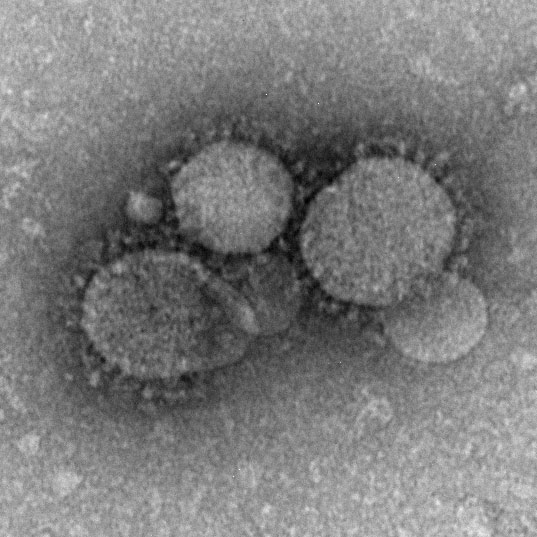
An electron microscopic image of the virus causing MERS. Source.
MERS (Middle East respiratory syndrome) is caused by a virus which appears to have jumped from camels to people and can now spread between people. It was first detected in the Middle East in 2012. Health officials are keeping a close eye on it. Read more in the news link below:
ABC News: CDC Confirms First Case of MERS in US
![[describe image in words]](http://america.aljazeera.com/content/ajam/multimedia/photo-gallery/2014/4/photos-battling-anebolaoutbreakinguinea/_jcr_content/slideShowImages/slide2/image.adapt.960.high.jpg)
“A health specialist prepares to work in an isolation ward where patients displaying symptoms of Ebola are held at the Doctors Without Borders facility in Guekedou, Guinea.” Source
A recent outbreak of Ebola in Guinea has experts worried and nearby West African countries watching their borders. Read about why — and what’s being done at Al Jazeera America (International W.H.O. says fight against West Africa Ebola outbreak just beginning) or listen at NPR (The Ebola Outbreak 3 Weeks In: Dire But Not Hopeless).

“The plate on the left contains about equal numbers of colonies of two different bacteria. After the bacteria compete and evolve, the lighter ones have taken the lead in the plate on the right.” Source
Do we ever stop evolving? Twenty five years — and some 50,000 plus generations — of ever-fitter bacteria suggest no. NPR ‘Shots’ has the story of how Bacterial Competition In Lab Shows Evolution Never Stops.
After being hospitalized for 2 months, Kali Hardig, 12, gets to go home after recovering from amebic meningoencephalitis which health officials believe she contracted at a Little Rock, Ark., waterpark in July. She is only the third known survivor of the deadly infection in the last 50 years. Read more at Daily News: Arkansas girl survives brain-eating amoeba

Closeup of new California ‘Vaccine Exemption’ form with the religious exemption option highlighted.
NPR has the story of How A California Law To Encourage Vaccination Could Backfire. A new form intended to require all parents to talk through vaccination risks and benefits with a health care provider before exempting their children includes an unexpected exemption of its own – one that challenges the law itself.

The new coronavirus as seen with an electron microscope. Note the characteristic halo, or ‘corona’, of proteins projecting from its outer surface. Source: NIAID/RML.
NPR has the story of the ongoing hospital outbreak of a novel coronavirus first isolated back in September. Like its cousin SARS, the virus some are calling MERS-CoV (Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus) causes severe, potentially fatal pneumonia in humans. Another troubling aspect of the new virus is that it may disrupt our immune system recognizing the cells it has infected [*]. The World Health Organization has the most recent updates available as part of its Global Alert & Response system.

“Reprogrammed cells (green) fuse with and become skeletal muscles (red), spreading infection as they go. Cell nuclei are shown in blue.” Source: Masaki et al./Cell
Recent research into the mechanisms of leprosy suggests that bacterium Mycobacterium leprae reprograms human Schwann cells to act as stem cell-like vectors for further infection. WIRED Science has the story.

Caption via New York Times: “Tiny magnetic beads force the larger T-cells to divide before they are infused into the patient.” (Photo: University of Pennsylvania)
The HIV virus causes AIDS, one of the top ten causes of death worldwide. It is also the surprising key to a new cancer treatment with revolutionary promise. The New York Times tells the story.
![[describe image in words]](http://media.npr.org/assets/img/2017/02/01/title_ep01_wide-05ac79a0ebeb8ee9ba826864096789cdbf78b5c4-s400-c85.jpg) Xaver Xylophon for NPR
Xaver Xylophon for NPR
