This two-part editorial by the Insight team seeks to open a discussion between faculty, students, postdocs and the school administration about whether the school is prepared for meeting the changes in the future of PhD holders. The first part will address the current available resources and the unmet needs of the students/postdocs, and will also explore some possible solutions. The second part, to be published in the next issue of the InSight, will carry the opinions of all parties involved collected through a survey and communication, which will serve as a stepping stone towards meaningful changes that will benefit us all.
Editors’ Note, 4/11/16, 1:30 pm – The article has been modified to include corrected information regarding the BEST award application by Sackler. Previously it had stated that Sackler had applied for the BEST award and was not awarded due to lack of proper infrastructure. However, after communicating with the Dean’s office, we have learned that Sackler had applied in conjunction with other Tufts graduate schools and it is speculated the application was not funded partly due to complex administrative structure and evaluation and dissemination plans. The changes are reflected in the article.
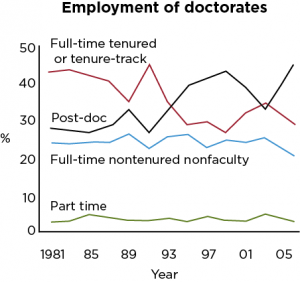
The Doctorate in Philosophy (PhD) is a degree awarded to recognize original contributions to collective human knowledge. Thus, it is no surprise that the next step after getting a PhD is to join the bastions where such knowledge is curated and cultivated, i.e., to pursue an academic career. However, given the current structure of an academic job and the nature of academic tenure, a bottleneck in academic positions have taken firm root in the last years. According to Nature, the number of postdocs have jumped by 150% between 2000 and 2012 while the number of tenured or full time faculty positions in the US has either remained stagnant or fallen. While the debate on how to improve the lives of postdocs and other non-faculty PhD holders rages on and restructuring of federal funding for scientific research is ongoing, the increasing number of PhDs leaving the traditional path and venturing into other professions is readily apparent.

In recent years, the PhD degree has been developed as a marketable asset with a accompanied with a powerful skill set — the ability to think critically, solve problems and troubleshoot, be organized and detail-oriented. The idea that the skills required for obtaining a PhD are also recognized as required to be successful in any other profession, and is now being echoed by career counselors. While industry research positions were once spoken about in hushed voices before, these positions are now not only coveted, but other non-research jobs are also becoming more prominent in seminars and career advice panels for biomedical graduate students and postdocs.
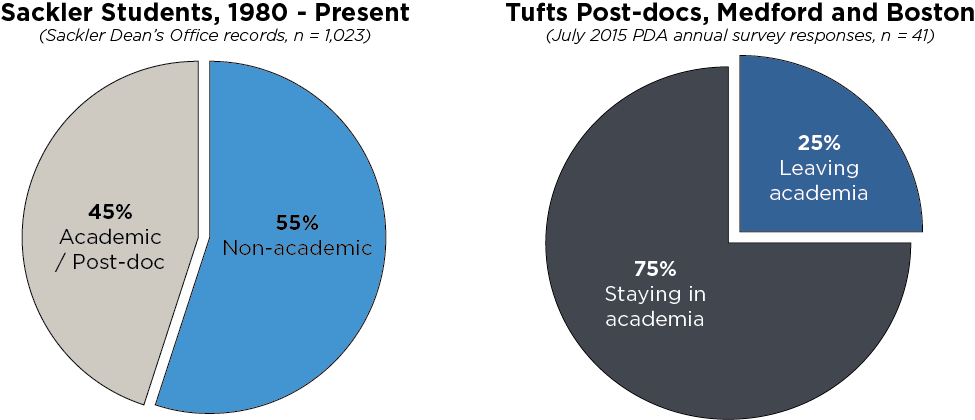
This trend is also evident within the graduate student population here at Sackler School of Biomedical Graduate Sciences, where more than half the alumni have pursued non-academic careers. As the funding climate struggles to recover and academic positions become more scarce, the question arises of whether the existing model of career development for student and postdoctoral trainees is sufficient to ensure future success and achieving their goals. It is apparent that career development training outside of academia is required, but the support for this by the curriculum and administration at the Sackler School seems to lag behind our peer institutions, and even our colleagues on the Medford campus have access to the Tufts Career Center and the students in the Fletcher School have their own Career Services office.
Resources currently available for students at Sackler interested pursuing non-academic careers are mostly driven and organized by the students themselves. These student-led initiatives have produced a full roster of seminars and workshops focusing on such career options held nearly weekly between the Career Paths Committee of the Sackler Graduate Student Council (GSC) and the Tufts Biomedical Business Club (TBBC). These groups have become increasingly active over the past few years, with their efforts growing into independent events like the Tufts New England Case Competition (TUNECC), as well as collaborations with the Tufts Postdoctoral Association and student groups in the School of Medicine. Additionally, the Tufts Mentoring Circles group has provided students peer guidance and spaces to discuss such career options among themselves. Every student initiative listed here has sought more interactions with Sackler alumni, but the information to facilitate that exchange is not readily available. Student leaders at Sackler have expended great effort to build the career resources the student body needs, but these efforts are reaching the limit of what they can achieve and will only be short term and partial solutions without additional resources and support infrastructure. Some of this could be built by students, like shared repositories for maintaining records and thus institutional memory so energy is expended solving new problems instead of rehashing old ones. The most important piece, however, cannot be done by students alone: an accurate, current database of Sackler alumni and their occupations that is accessible and searchable.
We appreciate that the Dean’s Office has recently increased its support of these student efforts, but believe that more can be done. An increased contribution to co-sponsorship from partial funding of one or two events with the GSC annually to a series of three annual workshops and career panels over the past two academic years, and the interactions between a handful of students with Sackler alumni through the new “Day in the Life” program are good starting points. However, the student body and Sackler as an institution would derive greater benefit and return on an investment in career development and advising staff, similar to those available at the Fletcher School and the Medford campus, but scaled for Sackler. It would be mutually beneficial, as it works to the advantage of a school to have an engaged student body that will recognize and appreciate the school’s support in shaping their careers as alumni. Furthermore, this infrastructure could be a common point for alumni to rely upon and connect with students and each other.
The lack of formal career development resources at Sackler has been identified by peer reviewers as an area for improvement, and puts us at a competitive disadvantage for student recruitment and securing grant funding. Prospective students actively seek graduate programs that provide career development, and among the recommendations made by the review committee for the newly-merged CMDB program were formal non-academic career training options and an expansion of extramural internships through the alumni network and faculty connections. Funding agencies such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH) evaluate grant applications on this aspect of graduate training as well. For example, F31 grant applications to support graduate students require descriptions of career training and development; the proposed changes will essentially strengthen the Sackler students’ applications and may increase the number of extramurally funded students, alleviating the pressure on the school. A more recent example includes the NIH Broadening Experience in Scientific Training (BEST) awards, a funding opportunity established in 2013 in response to the state of the biomedical workforce and to prepare trainees for diverse career paths that utilize their PhD training. Boston University received a BEST award in 2014 for its biomedical research programs in part because of its existing career development and support infrastructure. It should be noted that Sackler, along with other graduate schools at Tufts, had applied for the BEST award. While the reviewers had found the application to be strong in certain areas and to have “potential for high impact”, they also noted weaknesses that included “complex administrative structure and the evaluation and dissemination plans”, which could partly be responsible for the award not being funded (source – email communication with Sackler Dean’s office). These issues can be addressed with the establishment of the proposed infrastructure development and can further strengthen such grant applications in the future.
The faculty mentor plays an important role in shaping a mentee’s future career — the mentor’s support and guidance are essential for the mentee’s career development. While Sackler faculty are generally supportive of students and postdocs, it is critical for them to come forward and actively support mentees’ who choose to pursue careers outside of academia and research. The Greater Boston area is known as a hub for biotechnology research and business, with companies specializing in everything from drug development to consulting. Many recent and local alumni maintain a connection to Tufts through their faculty mentors absent a career development office at Sackler, and both students and postdocs would greatly benefit if the faculty mentors shared these connections, and offered guidance and support on leaving academia.
The current funding climate and the stagnation of academic positions, along with the burgeoning postdoc crisis, amount to conditions favorable for a paradigm shift. We cannot just keep focusing on the academic jobs traditionally held by PhDs. In order to better adapt to this changing landscape of post-doctoral work, the students, postdocs, faculty, and administration need to work together to bring about improvements to the environment at Sackler, specifically:
- Developing an accessible, searchable, up-to-date database of Sackler alumni that can be used by students, postdocs and faculty looking for career advice and connections.
- Faculty support in the form of guidance and connections in developing non-academic careers.
- Career development support staff for students from the Tufts and Sackler administration, so as to cultivate an engaged alumni population.
Comments, suggestions, and other feedback on this editorial can be left on either the InSight blog or via this online form: Anonymous feedback form: http://goo.gl/forms/PXEfcLfgeX
A survey to collect more detailed data from the student body will be conducted by the Sackler GSC in the coming weeks.