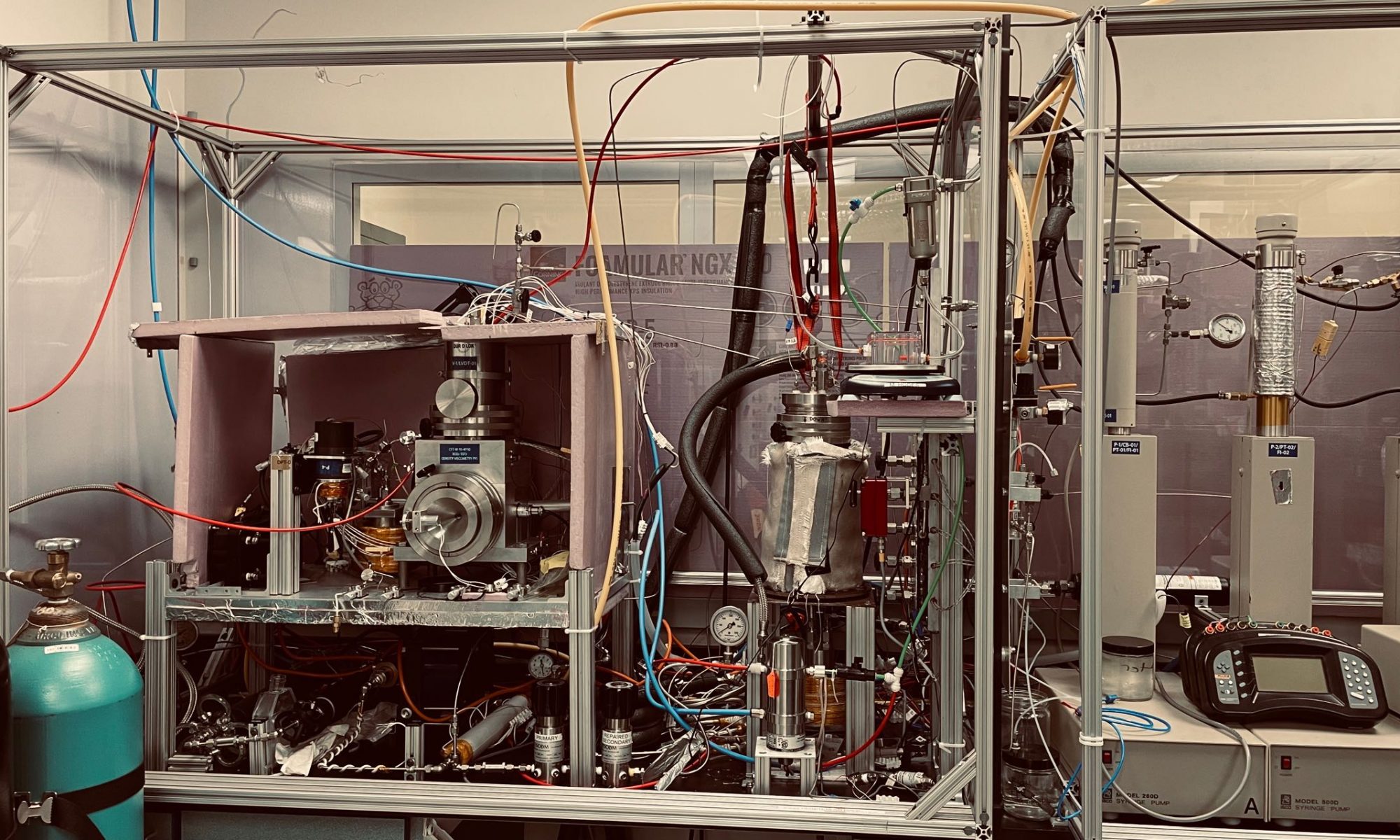
[latexpage]Permeability $K$ is an indication of the ability to allow fluid (gases, liquids, and supercritical fluids) flow path through porous material, described by Darcy’s Law per $$ \vec{u}=-\frac{K}{\mu} \nabla p $$ where $ \vec{u} $, $ \nabla p $, and $ {\mu} $ is the flow velocity, pressure gradient vector, and viscosity, respectively. Permeability is usually considered as a constant depend only on porous bodies geometrical feature. However, nanoporous aerogel do not exhibit this behavior, as its flow regime is characterized by the Knudsen number (Kn = mean-free path of fluid molecules / pore size of aerogel). Most permeability data in literatures are measured at ambient conditions using air or water, thus not useful for supercritical fluids.
We developed an experimental apparatus that can measure the permeability of aerogel at both ambient and supercritical conditions, using two redundant methods.

The permeability of aerogel is measured by two independent methods using the experimental apparatus shown above. First, it’s measured by a direct method where the fluid is pumped directly through the aerogel and the permeability of the aerogel can be extracted from the measured pressure drop across and the flow rate through it.
Secondly, it’s measured by an inverse method where the permeability is inferred from the relaxation time of the pressure reading for a step increase of pressure, inside a vessel with a sudden decreased volume.
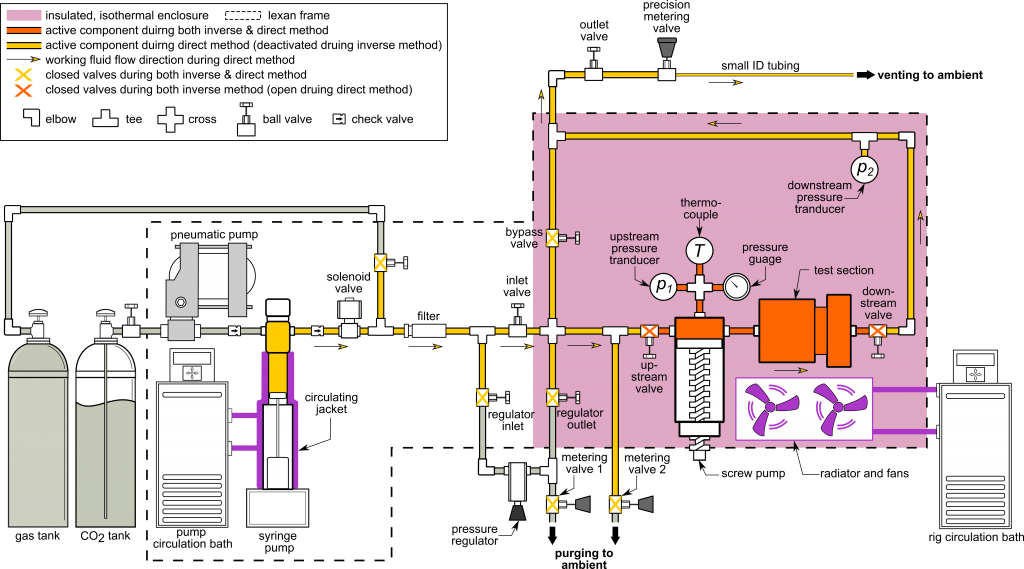
Direct Method
compute permeability using Darcy’s law for 1-D steady flow per $$K = \frac{{\mu QL}}{{{A_{\text{c}}}\Delta P}}$$