Thinking about design thinking
I’ve had some exposure to design thinking both professionally and as a student but it has always involved developing a usable product, either physical or digital. It wasn’t until I attended a session at the 2019 NEMA Annual Conference that I realized its potential for programming purposes. In hindsight, that’s an absolute “duh!”
In a session titled Using Design Thinking to Solve Problems Throughout the Museum, Sherlock Terry, Trish Palao, and Jennifer Rickards of the Montshire Museum of Science shared examples of using design thinking for a range of projects including exhibit design, operational challenges, and event planning. They introduced the room to the basics of design thinking, walked attendees through the steps in three Montshire use cases, and then we had the chance to practice it ourselves. (Hands-on learning – my favorite!)
The idea behind design thinking is that it is a human-centered approach. It’s flexible, iterative, and, as most design thinking proponents will tell you, usable by most anyone. It’s not exclusive to people who identify as designers professionally or as a hobby. I’d wager many professionals follow the process intuitively, but may not hit each stage.
The typical order for the five stages is as follows:
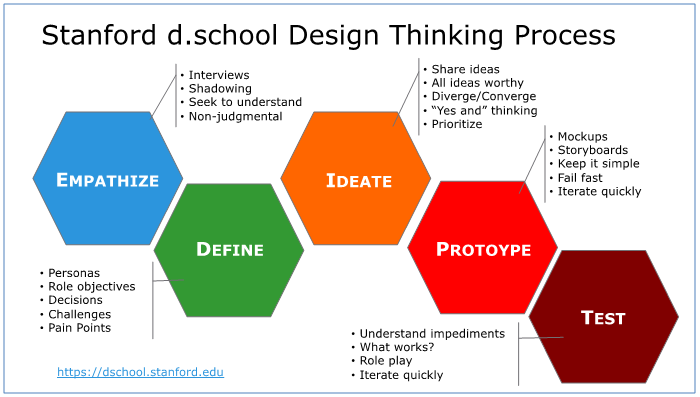
The stages can happen in order, out of order, and repeat as many times as the project requires. Understand your users from their perspective, clearly define what it is they need, brainstorm ways to help, and do a practice run (or three) to see if the project achieves what you hope it will.
This graphic from the Interaction Design Foundation illustrates the cyclical nature of the process:
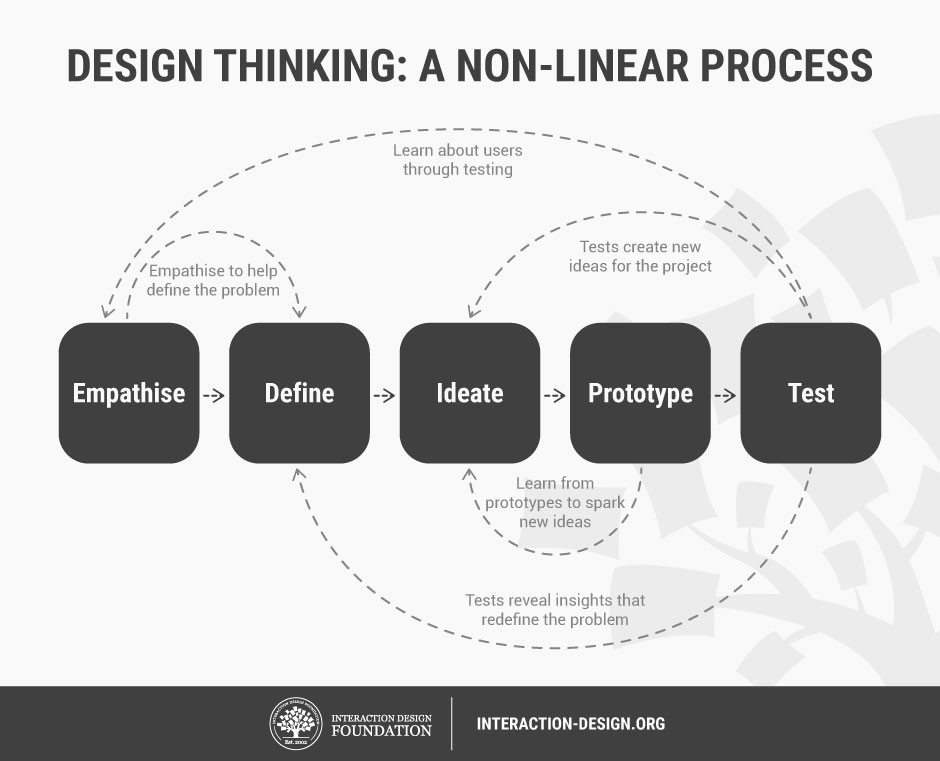
Design thinking’s focus on user needs and flexibility makes it the perfect multipurpose tool for just about any challenge we might encounter in museum work. As our work is entirely for the sake of our visitors, if our project doesn’t work for the people we serve, it doesn’t work at all – no matter how cool or innovative we think it might be.
If you’re new to design thinking, here are a few helpful tips I’ve learned courtesy of both Montshire staff and the Tufts digital media course:
- Enter the process with a well-defined goal to guide you. Our broad goal for the practice scenario in the NEMA2019 session was “How can our museum better engage teens?”
- There are multiple ways to think of the problem you are defining – without thinking of it as a problem. Consider it a “job to be done” or build a challenge statement. Montshire staff gave us this template for a challenge statement:
- How might we [theme goal] in order to [broad goal] considering that [key consideration #1] and [key consideration #2].
- Example: “How might we train staff in order to better engage teens considering that staff may have little knowledge and/or negative impressions of that age group?”
- When brainstorming, go big and broad. Montshire staff came up with 40 ideas during their ideate stages! The idea isn’t to have 40 winners, but to spit out anything that comes to mind. Ideas which might seem totally bizarre or unattainable may have just the right kernel of inspiration.
- Post-its are your friends here: use one post-it per idea and then group them into themes.
- Prototypes don’t have to be physical. Develop the prototype that fits your goal – if you’re designing a program, this might be a lesson plan, a discussion prompt, a question on a sign, a game, a worksheet, whatever. Whatever format lets you test if users are getting what they need is the right format.
Here are some additional resources on design thinking and design thinking in museums:
- Design Thinking for Visitor Engagement: Tackling One Museum’s Big Challenge through Human-centered Design
- Embedding Design Thinking in Museums
- What is Design Thinking for Museums?
- Program Perspective: Design Thinking
- An entire site dedicated to Design Thinking for Museums
- What is Design Thinking and Why is it So Popular?
- Put Design Thinking to Work: Design Thinking Mixtapes
What uses have you gotten out of design thinking? We’d love to hear your experience in the comments!