Histone Acetylation Mechanism
Enzyme: Histone Acetyltransferases (HATs) (Fig. 1)[17]
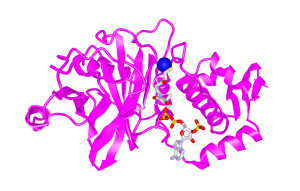
Figure 1. Histone Acetyltransferases (HATs)[17]
Histone acetylation consists of the following steps (Fig. 2)[11].

Fig 2. Histone Acetylation Mechanism[11]
- A glutamate residue on HATs acts as a general base and activates the lysine ε-amino group by deprotonation. Nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl group of acetyl CoA.
- A tetrahedral intermediate forms, and then collapses with the loss of coenzyme A (CoASH) through elimination. The lysine residue on the tail of histone is acetylated and loses its positive charge [16].
November 13, 2017 at 8:22 pm
Straightforward page, looks good!