Specific Aims
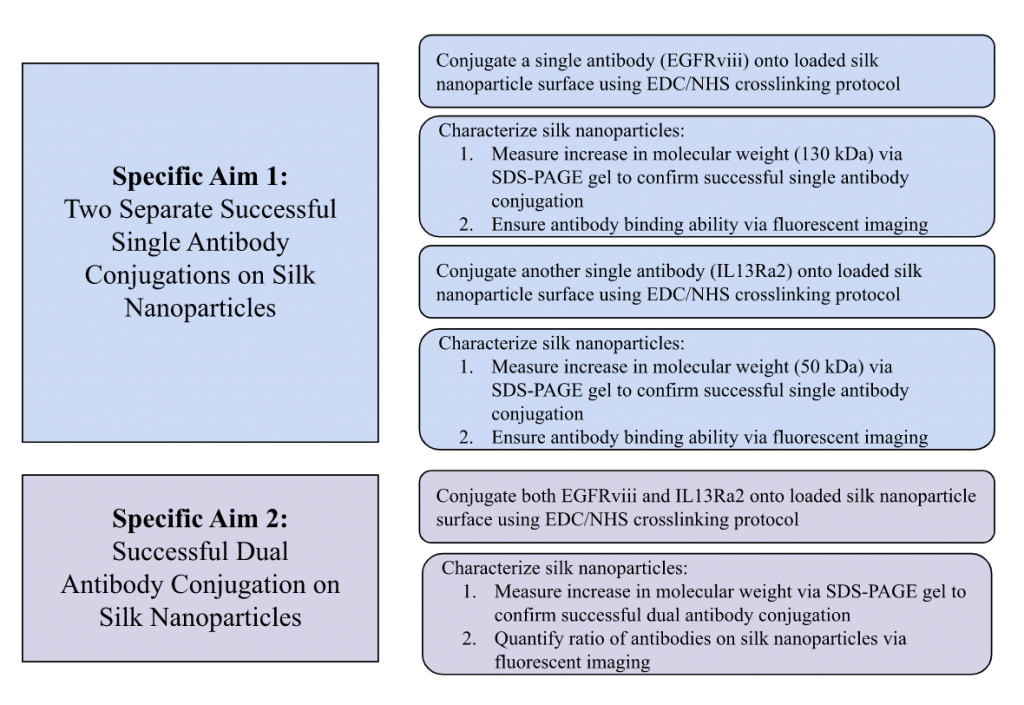
Specific Aim 1: Conjugate Anti-EGFRviii and Anti-IL13Ra2 Separately
In Specific Aim 1, antibodies anti-EGFRviii and anti-IL13Ra2 will be conjugated onto silk nanoparticles using EDC/NHS conjugation. EDC/NHS was chosen due to its prevalence in literature for analogous platforms. Using EDC/NHS protocols and materials available in the Kaplan Lab, antibodies will be conjugated onto silk nanoparticles in two separate experiments. It is expected that all nanoparticles will be conjugated with the antibodies. It is also not highly likely that only a portion of nanoparticles will successfully conjugate to the antibodies; therefore, there is no need to isolate these nanoparticles successfully conjugated from the rest of the population. We will treat anti-EGFRviii and anti-IL13Ra2 nanoparticles with secondary mouse and rabbit antibodies respectively and use a Keyence fluorescence microscope to visualize fluorescence that would be present if conjugation to nanoparticles occurred. A plate reader will also be used to determine the concentration of antibody present by measuring the emission and excitation of the fluorescent secondary antibody. If time allows, additional experiments using ELISA can confirm specific binding. Conjugation will be deemed successful based on the visualization of secondary antibody-tagged nanoparticles compared to that of the control of nanoparticles coated in secondary and the standard curve. As of right now, there isn’t a way to label some aspects of the population with a level of quantification without the use of flow cytometry. However, two potential options our group is looking at are (1) Finding a percentage of original concentration that was maintained overall (in our case, we calculated that 3.9% of original concentration was maintained in our IL-4 test run) or (2) Using DLS size difference to quantify the unconjugated nanoparticles with the conjugated nanoparticles.
Specific Aim 2: Dual Conjugation of Anti-EGFRviii and Anti-IL13Ra2
Specific Aim 2 will produce dually conjugated silk nanoparticles with anti-EGFRviii and anti-IL13Ra2. Dual conjugation was chosen due to previous literature linking it to enhanced therapeutic efficacy in tumor models{Mi, 2018 #113}. We follow EDC/NHS and fluorescence protocols established in Specific Aim 1 to conjugate both anti-EGFRviii and anti-IL13Ra2 antibodies onto silk nanoparticles as the protocol for dual conjugation is the same as the protocol for single conjugation. We are not expecting that conjugation of one antibody will interfere at all with the conjugation of another due to previous literature in the field. In terms of analysis, the means of our dual conjugated silk nanoparticles will be compared to that of our single conjugated silk nanoparticles. To confirm antibody binding and concentration, the nanoparticles will be treated with secondary mouse and rabbit antibodies for plate reading. It is known that silk nanoparticles experience some small amount of autofluorescence, as silk scaffolds do, but not by that much where it would interfere with plate reader measurements with our secondary antibodies. The fluorescence in each well plate will be qualitatively analyzed in comparison to all conditions. If time allows, anti-IL13Ra2 and anti-EGFRviii will be bound in different test ratios to determine nanoparticle surface coverage. To start, equal concentrations of each antibody will be tested and adjusted as our experiment progresses.
Leave a Reply