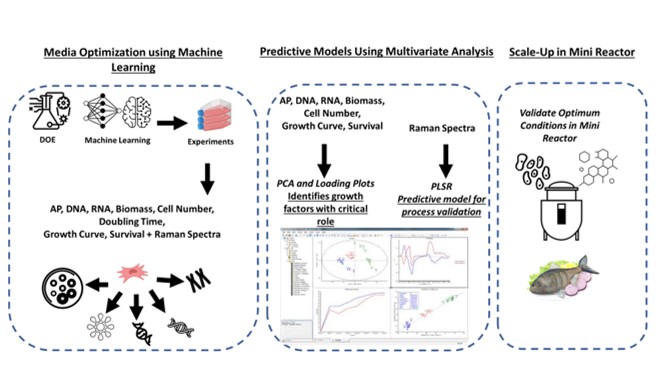
The overarching goal of Aim 5 is to develop serum-free media that is economically viable for cell proliferation and differentiation to optimize the development of low-cost and robust defined serum-free media.
• bioprocessing
• ingredients
• recycle
• molecular modeling
Bioactive Protein Sources – utilize bioprocessing (enzymatic digestion) methods to generate bioactive peptides for cost-effective serum-free media
Generate and Characterize Protein Hydrolysates – screen and characterize protein hydrolysates (e.g., from insects, algae, yeast, marine byproducts, plants, and agri-wastes – enzymatically hydrolyzed
Assessments in Cell Culture – evaluate protein hydrolysates towards muscle and fat cell culture goals
Modeling – apply machine learning to develop and optimize low-cost serum-free growth media for cell-lines to optimize processes