 TongRO Images/Corbis
TongRO Images/Corbis
Brain cells that track our location also can track time and distance, a new study published in the journal Neuron finds. This could explain how the brain uses place and time to organize memories throughout our lives.
Read more at NPR.org.
 Leigh Wells/Ikon Images/Getty Images
Leigh Wells/Ikon Images/Getty Images
When you have to remember many things at once, you might try to juggle all those to-do items in your head simultaneously. But new scientific research published in the journal Nature suggests there might be a better approach.
Read more at NPR.org.
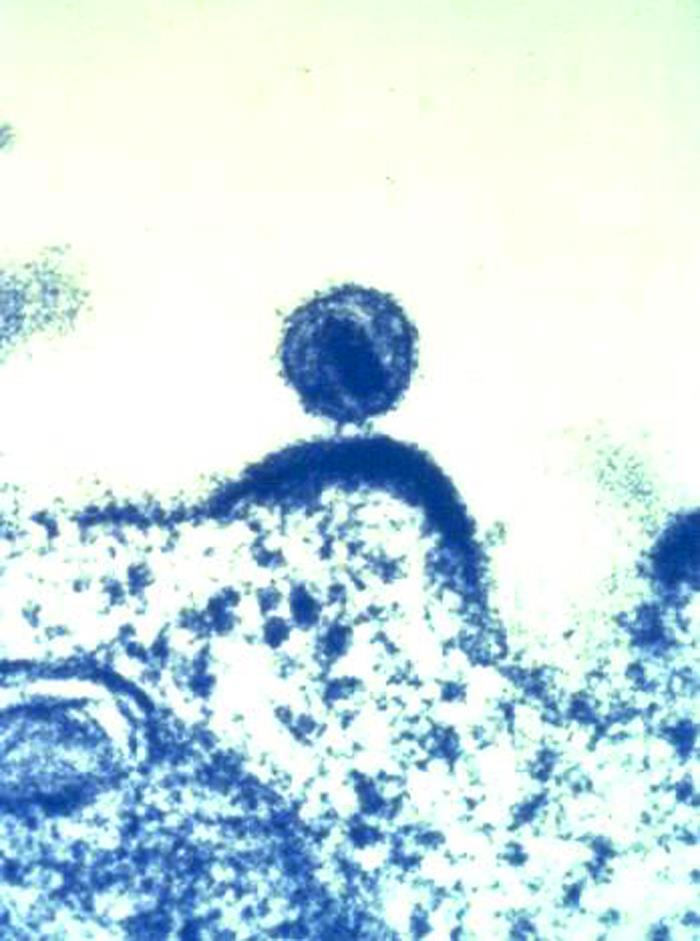
HIV particle budding from a cell. Image by the CDC.
When thinking about human viruses, we usually associate them with terrible diseases such as AIDS, measles, and Ebola. Bacteria were viewed in the same way when people discovered that they were the cause of many infectious diseases. Later, it became evident that many bacteria who live on and inside our bodies are beneficial. Could the same be true about viruses?
This article describes recent research about a virus named GB virus-C that may actually be beneficial for some people infected with HIV and possibly Ebola. However, more research is needed before final conclusions can be drawn.

A measles outbreak linked to Disneyland has nearly doubled in size since last week with 45 reported cases in California and seven more illnesses confirmed in at least three other states and Mexico. A contagious disease expert contends that the recent spread of measles is being fueled by a portion of parents who refused to vaccinate their children — an estimated one in 10 people today is perhaps susceptible to the virus.
Measles is very infectious because it spreads through the air, so you can catch it by standing next to someone who is infected. Initial measles symptoms include fever, cough, running nose and red eyes. After a few days, a red rash appears on the face and then spreads downward to the rest of the body. Measles can be serious and even fatal for small children.
Read more at NBCNews.com.
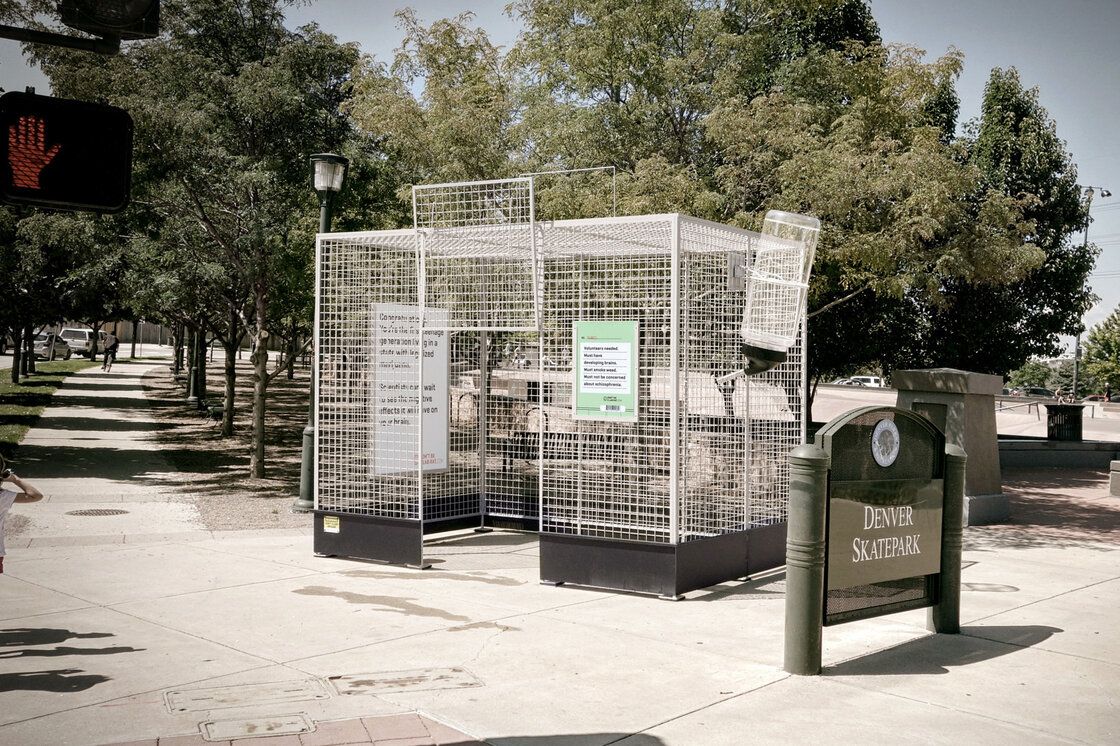

Public health officials in Colorado are facing an unprecedented challenging: explaining to teens why they shouldn’t smoke marijuana after the state legalized it. Campaigns against teen drug use usually rely on the scientifically proven health risks, but the studies on the risks of marijuana, especially to the developing teen brain, are still in their preliminary stages. Colorado’s public health campaign hinges on that exact idea and tells teens “Don’t be a lab rat”, complete with human-sized lab rat cages.
Read more about Colorado’s public health campaign at NRP.org.
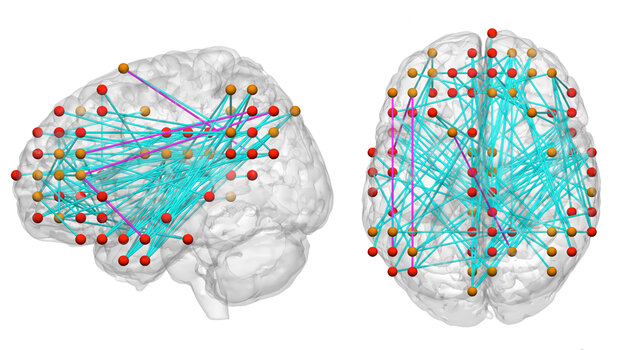
New research suggests that the neural network that controls attention may develop more slowly in children who have attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). While previous research suggested that the brains of children with ADHD develop more slowly, this new research was able to detect changes in connectivity within and between key brain regions.
Read more about the research at NRP.org.

Marijuana is the most widely used illicit drug, and more teenagers and young adults are using the drug in states that have made it available for medical use. Yet, several studies suggest that marijuana use during the teenage years can dampen the development of brain regions critical for memory and problem solving. In one study, researchers analyzed the effect of marijuana use on IQ. The researchers found that people who began using marijuana in their teenage years and continued to use marijuana for several years lost about 8 IQ points from childhood to adulthood. Read more at NPR’s coverage: Marijuana’s effect on Teenage Brain

The anti-bacterial resistant superbug MRSA has been documented in the U.S. food supply, but until recently other countries have yet to find the superbug in their food. Unfortunately MRSA has recently shown up on a poultry farm in the U.K., which may be the first sign that MRSA is taking over the U.K.’s meat industry as well.
Overuse of antibiotics in the food supply is blamed for the development of the resistant strain of bacteria. Constant exposure to antibiotics kills off the strains of bacteria that are affected by the drug, leaving the stronger, resistant strains to take over. These resistant strains can spread from livestock to humans working with the animals either at the farm or at the slaughterhouse, causing a risk for human disease. Some bacteria can also travel to produce growing nearby via migratory animals or irrigation systems. In the U.S., the Food and Drug Administration is attempting, for the first time, to limit the use of antibiotics in meat production. Under the new policy farmers and ranchers are no longer able to use antibiotics to make animals grow larger, a practice that is commonplace today. Farmers and ranchers will now need a prescription from a veterinarian to purchase antibiotics, a large change from the current practice where antibiotics are available for purchase at animal feed stores.
Click here to read more about the MRSA found in the U.K. poultry farm, and here to read about the FDAs decision to restrict antibiotic use in livestock in the United States.
Kidney disease is one complication that can arise in people with diabetes. It has previously been posited that the extra blood glucose in diabetes damages the kidney through a toxic molecule called superoxide anion. Research at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine has recently found that this is not the case. By analyzing the amount of superoxide anion produced in the mitochondria of diabetic mice, researchers have discovered that LOW concentrations of superoxide anion are associated with diabetic kidney disease, and HIGH concentrations of superoxide anion are associated with less markers of diabetic kidney disease. This discovery changes the field of diabetic research, and may lead to better understanding of diabetic kidney disease. Read more about this discovery, as well as possible explanations for how diabetes may cause kidney disease here.


Closeup of new California ‘Vaccine Exemption’ form with the religious exemption option highlighted.
NPR has the story of How A California Law To Encourage Vaccination Could Backfire. A new form intended to require all parents to talk through vaccination risks and benefits with a health care provider before exempting their children includes an unexpected exemption of its own – one that challenges the law itself.
Guest blogger Gina Cairney reviews the Great Disease Project on the Education Week blog Curriculum Matters: Infectious-Diseases Program Engages Students in Science:
At a time of heightened attention to getting students more engaged in STEM learning and careers, a recent initiative called the Great Diseases Project seeks to answer that call by exposing high schoolers to real-world problems that require the use of scientific ideas and practices.
A forthcoming Academic Medicine paper on the Great Diseases Project by Dr. Jacque et al. is featured in the AM Rounds March Sneak Peek.
workbook
Posted on August 22, 2012 by Berri Jacque | Categories: Uncategorized | |
|
Workbook
Posted on by Berri Jacque | Categories: Uncategorized | |
|
Hello world!
Posted on February 8, 2011 by Ilene Chen | Categories: Uncategorized | |
|
Welcome to sites.tufts.edu. This is your first post. Edit or delete it, then start blogging!
 TongRO Images/Corbis
TongRO Images/Corbis

 Leigh Wells/Ikon Images/Getty Images
Leigh Wells/Ikon Images/Getty Images






