While you’ve been hunkered down at home, have you seen any bumble bees in your urban yard? Maybe you’ve even seen a bumble bee nest! We want your help in scouting out the bumble bee nests of the urban greater Boston area.
TPI scientists have been hard at work trying to learn about the nesting ecology of bumble bees (Bombus spp). Bumble bee nests are the focal point of reproduction. In early spring, the queen emerges and forages alone for pollen and nectar. Then, she produces workers which take on foraging tasks, and the colony grows exponentially. Late in the season, as the colony begins to senesce, males and new queens are produced. After mating, males die and queens overwinter underground to start the cycle over.
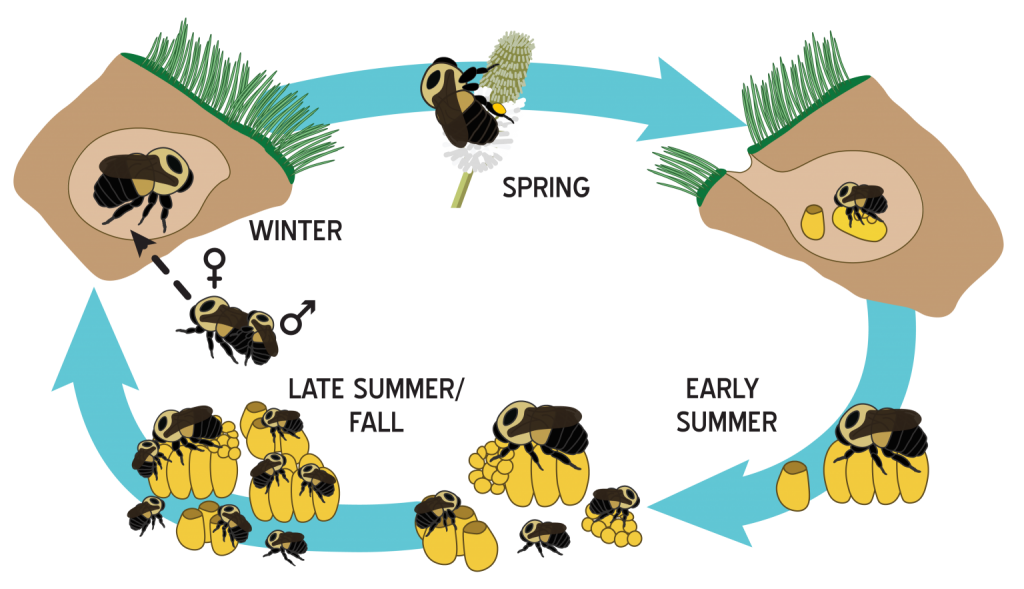
We have learned a great deal about bumble bee nesting in natural areas, but now it’s time to take that work into the city. Preliminary results already suggest that bumble bee reproductive ecology may differ between natural and urban environments, and we want to explore this further. Bumble bee nests can be difficult to find, but that’s where YOU come in.
Do you think you’ve seen a bumble bee nest? We want to see it! Bumble bees are cavity nesters, meaning they nest in small openings, such as crevices in rock walls beneath garden sheds. If you see frequent traffic of worker bumble bees (~1 bee/minute) to and from a single location, chances are you found a colony!

If you think you have a bumble bee nest in your yard, or know of one in the greater Boston area (within 15 miles of the Tufts Medford-Somerville campus), take a photo and get in touch with us by filling out this survey.
Thank you in advance and we look forward to hearing from you!


Maybe sightings of bumble bees, did not look for nests.
At the flower garden behind the veterans memorial on Winthrop Street, on salvia.
On the lobelia at 598 Winthrop and next door on the hollyhock.
Under the Shade of the 200 year old elm at Rural Ave and Crocker Road small island planting on the pink bee balm.