(67)
Vašková, J.; Vaško, L.; Mudroň, P.; Haus, M.; Žatko, D.; Krempaská, K.; Stupák, M. Effect of Humic Acids on Lead Poisoning in Bones and on a Subcellular Level in Mitochondria. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2020, 27 (32), 40679–40689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10075-w.
What is Humic Acid?
Humic acid (HA) is a classification for a group of molecules that are most commonly found in plant roots.67 These molecules help the plants to receive water and nutrients from the soil. HAs are most commonly found in humus soil. Humus soil is the soil formed from decomposing organic materials like plants and animals.68 This soil is abundant in nature, meaning HAs are also abundant.
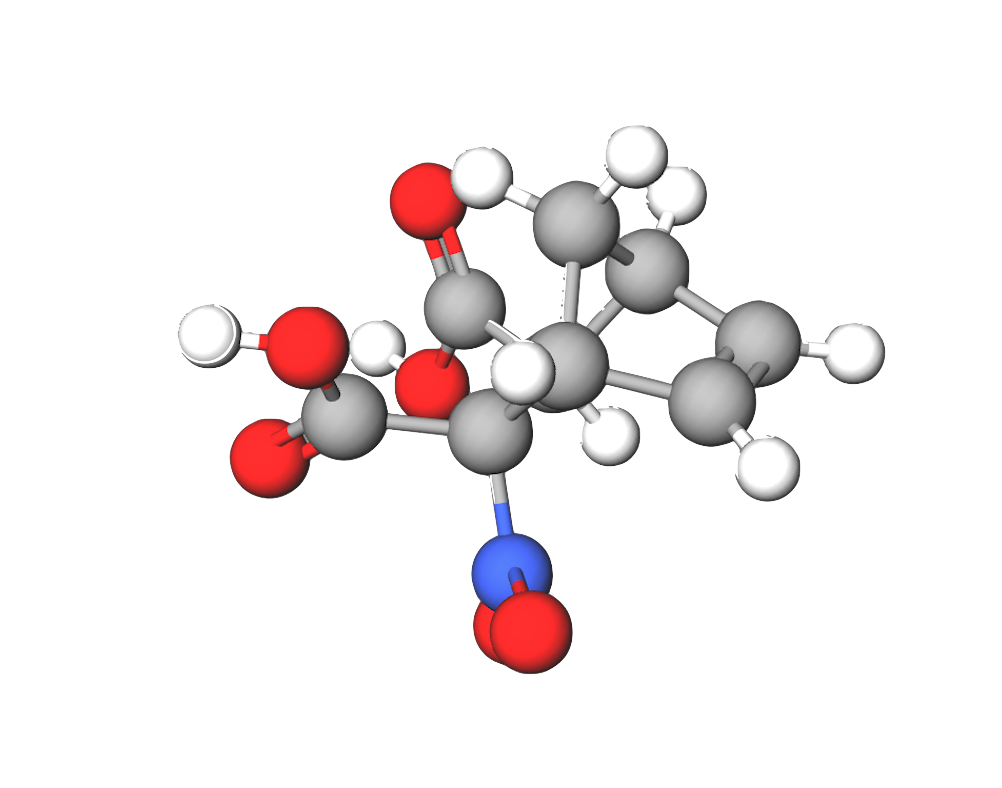
Figure 1 was created using molview.org.
Why Humic Acid?
Humic acids have been shown to have therapeutic effects, and thus their abundance is advantageous.67 HAs can act as unique ligands and display chelating activities to metal ions. Chelating agents have the ability to form a ring-like structure around metal ions; this changes both the properties and bioavailability of the metal ions. Chelation is used to treat metal poisoning because the ring-like structures make it easier for the body to excrete metals through the kidneys or liver.
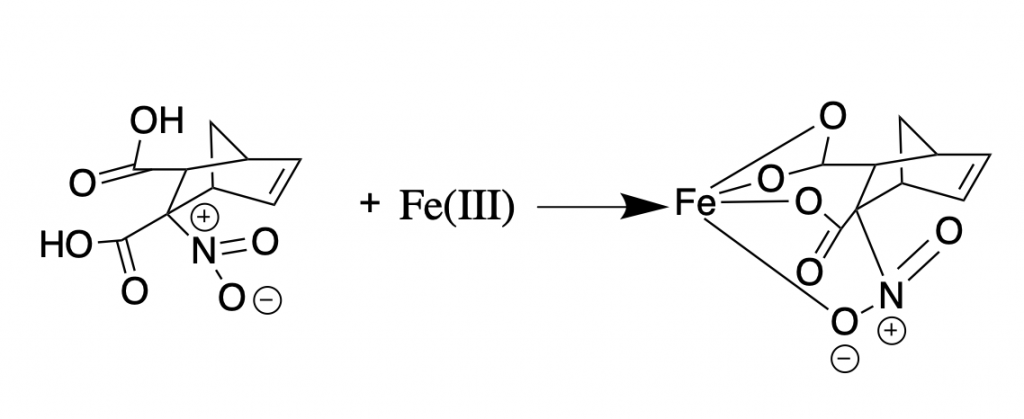
The purpose of this study was to examine the efficacy of humic acids as a treatment for lead poisoning, specifically in regard to lead accumulation and redistribution of other heavy metals in bone and mitochondria.
How was this Experiment Performed?
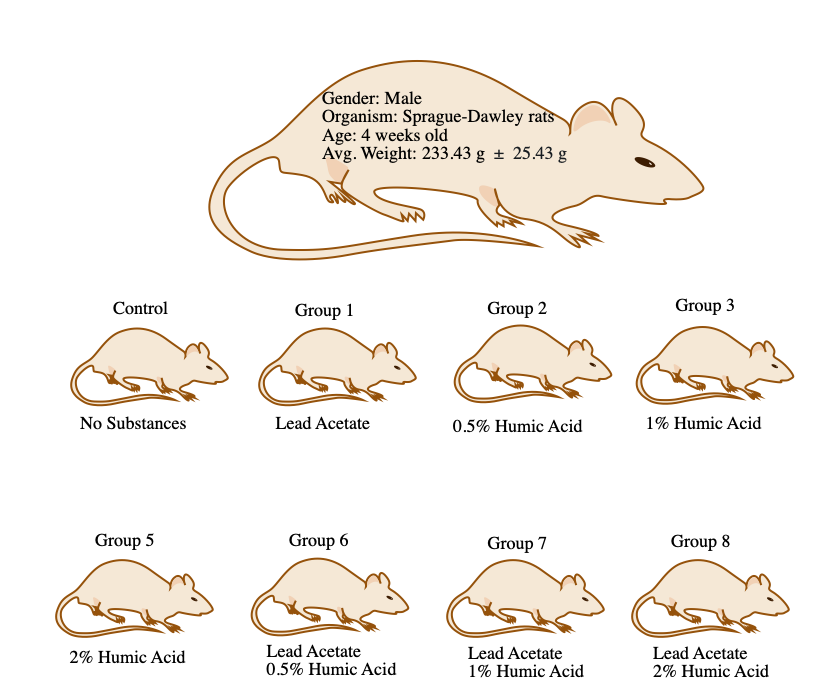
The rats were acclimated to the laboratory’s temperature and photoperiod. Then, in groups of 2-3 were placed in cages and were fed the same feed.67 To keep track of weight, the rats were weighed twice a week.67 There were around 30 animals in each group.67 During the first, fifth and tenth week, some of the rats were sacrificed and the left femur, heart, kidney and liver were removed to isolate mitochondria from each.67 Flame atomic absorption was used to quantify iron, zinc, and lead.67 Graphic Furnace atomic absorption spectrometry was used to quantify copper, manganese, and selenium. A t test, one-way ANOVA test and a Tukey HSD test were used to analyze the data.
What did the Researchers Find?
The results of this study indicate that the humic acids have potential to be a treatment for lead poisoning.67 After the first week, the rats that were administered HA (humic acid) with lead had less lead deposition in their femur compared to the lead only control group.67 Interestingly, the 0.5% HA administered showed a significant decrease of lead in bones and plasma.67 However, at higher concentrations like 1% HA, there was a decrease of lead in bones but an increase in the plasma.67
Through analysis of concentration of Pb in bones, the 1% HA was found to be the most effective treatment.67 After the fifth week, the rats with the 1% HA treatment had the lowest change in lead concentration.67 This means that the body was better at stabilizing lead levels with the 1% HA treatment.
In addition to the percent concentration, mitochondria were analyzed for lead concentrations. Researchers decided to analyze mitochondria because previous experiments showed lead poising caused inhibition of mitochondrial respiratory complexes by lead in rat liver mitochondria.67 These previous experiments confirmed that lead is deposited in organelles. Researchers in this experiment used the lead concentration in different mitochondria to measure the efficacy of each treatment. Both the 1% and 2% HA treatments led to the most significant downward treatment for lead in liver mitochondria.67
How Does HA Compare to Existing Treatments?
The aqueous leaf extract of Thunbergia laurifolia (TL) is another treatment of lead poisoning.21 This treatment, when tested in rats, was observed to not affect the lead level in the blood or brain.21 However, it did alleviate some of the adverse effects, such as memory loss.21 The treatment with lead caused alterations in expression levels of various antioxidant levels, which is a marker of lead induced oxidative stress.21 This shows that it does not have chelation properties since the lead levels do not decrease with the administration of the treatment. The TL aqueous extract caused the plasma SOD levels to remain the same while the antioxidant capacity in the plasma increased.21 This means it is likely the TL aqueous extract can reduce the oxidative stress in the brain and can improve SOD and GSH-Px activities which in turn alleviates the memory loss and learning deficits that come with lead poisoning.
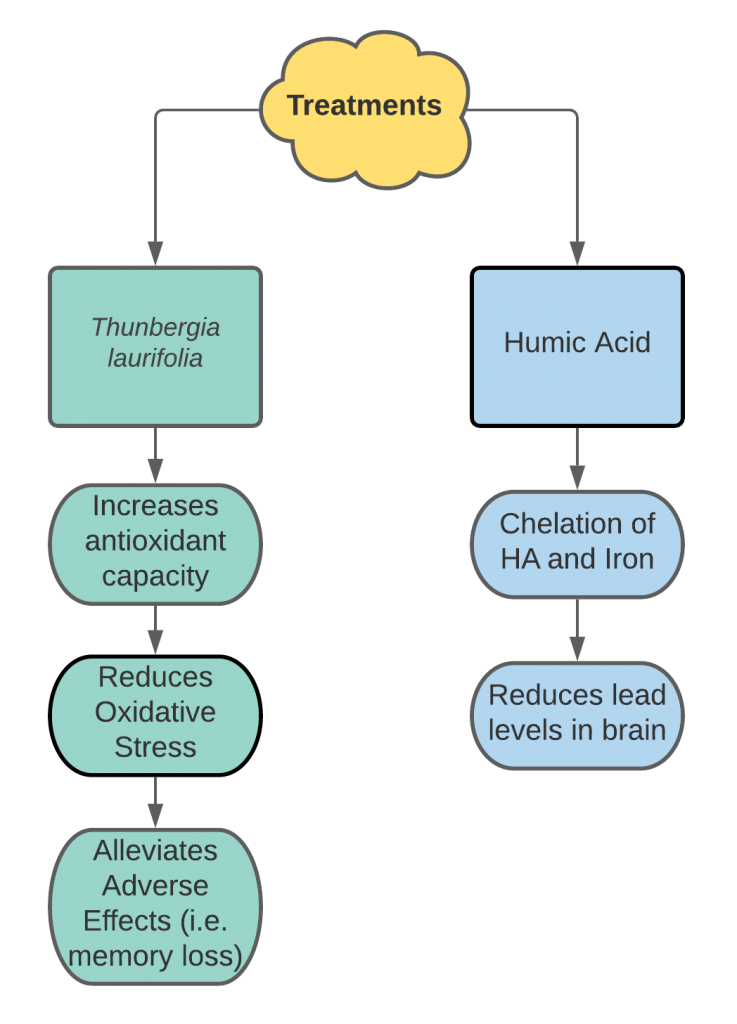
An interesting future study would be to investigate the impact of using both these treatments at the same time, as they affect two different areas: adverse effects and lead levels.
“Chelation is used to treat metal poisoning because the ring-like structures make it easier for the body to excrete metals through the kidneys or liver”
Maybe go into this a bit further into this idea (theory as to why it happens) or if you can cite references that touch upon this that would work as well.
Could use an extra one or two sentences at the end of the “Why Humic Acid?” section to introduce the experiment and briefly explain the research goals (to use Humic acid as a treatment for lead poisoning). It feels a little abrupt to move straight into “How Was This Experiment Performed?”
Similar comment to your pharmacokinetic model page, I was wondering why you left the reference to the research paper here? I guess it’s fine since you purposefully left those citations at the top of the page.
How does metal chelation by the Humic Acid allow the excretion of metals like lead through the kidney and liver? Also, it may be beneficial to go into further molecular depth when explaining this process of chelation.
A description of which specific symptoms the humic acid treatment could help alleviate could make it easier to make a comparison between it and the TL treatment, as it is stated that TL helps with the memory loss due to it reducing oxidative stress on specific biomolecules that are connected to learning and memory. However, if this was not given in the paper, that’s perfectly fine. I agree that a future study testing how both of these treatments work when combined would be interesting. Additionally, how recently was the TL treatment developed? Has it been tested in humans yet? (not all of these questions need to be answered on the page; just some things I was curious about that you could consider including)
Thank you for your comment! I tried to look into if it has been tested into humans and I could not find that information.