The body expresses four opioid receptor subtypes on central and peripheral neurons: µ, κ, δ, and opioid receptor-like 1, of which µ and κ are the best understood (4). Clinically prescribed small molecule pain-relief drugs like morphine and illicit derivatives like heroin target µ receptors. They cause possible side effects such as euphoria (which gives them addictive potential) and respiratory depression (which can be lethal) (4). Activation of κ receptors relieves pain without these secondary consequences, but has its own side effect profile which includes dysphoria and sedation (5). However, κ activation’s side effects are mediated only by the central nervous system, making agonists that exclusively bind to peripheral κ receptors attractive as minimal-side-effect analgesics. Peptides are excellent candidates for this, given their reduced potential compared to small molecules to cross the blood-brain barrier that divides the central and peripheral nervous systems (5). Peptide κ opioid receptor agonists therefore show great promise as efficacious painkillers with minimal adverse side effects or liability for abuse.
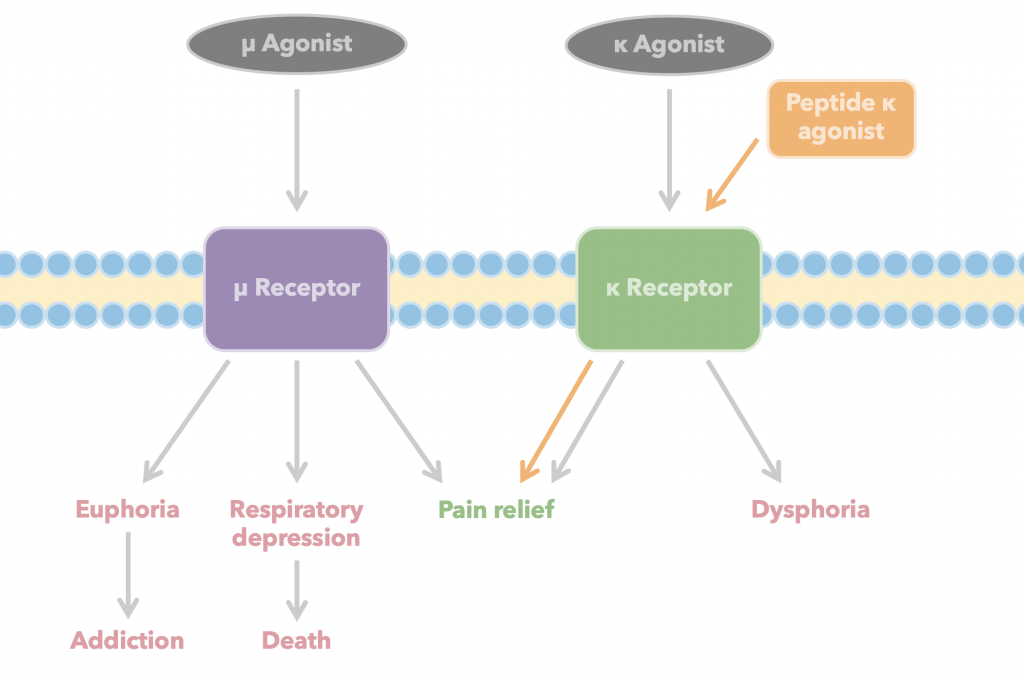
This page is factual and to the point. I would include the greek letters for the receptors instead of their English spelling, but it looks good and gives a good explanation for what the receptors do.
All fixed! The titles of the mu and kappa receptor pages still have them spelled out because the site wasn’t happy with lowercase greek letters in the heading buttons.
To me this page seems like the a mechanism page, rather a solution or answer to the question you prompted. In a way yes it can serve as a solution but maybe label this page as a mechanism page under this page.
That definitely makes sense! Our answer is sort of inherently mechanistic, but we wanted to keep it titled as “the answer” to make it clear that the answers to the questions we pose in the first page can be found here.
It could be good to include a sentence about either the potential or lack of potential in both delta and opioid receptor-like 1 agonists. Something as much as “only mu and kappa receptors have this pain relief activity” but just so the reader knows how they play a role/why they’re mentioned in the first sentence. In terms of peptides vs. small molecules crossing the BBB, a visual on this page would be helpful for context for the reader.
We added a bit about how the other two aren’t super well-studied, and made “minimal side effect analgesics” hyperlink to the peptide analgesics page, where we include the figure you suggested. Thanks!