Transformation creates opportunities and problems that call for collective interpretation: What are we about? Who are we? What is important? What are our priorities?
(Eckel & Kezar, 2003a)
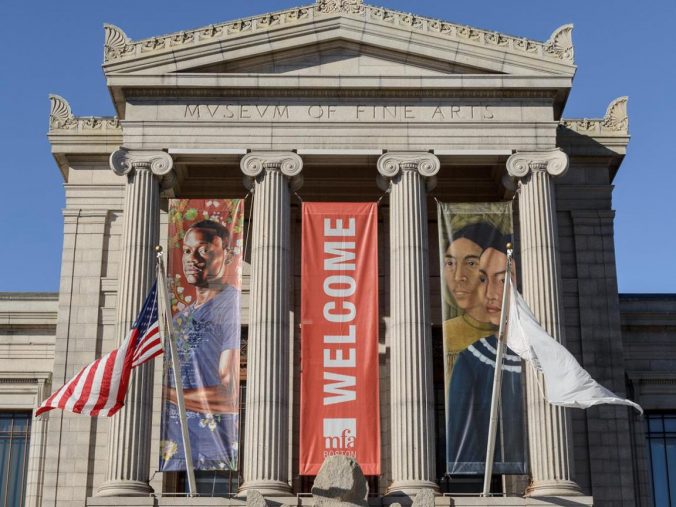
In May of 2019, a story of racist behavior directed at students of color at the MFA Boston broke on news sites across the internet. Seventh graders from Helen Y. Davis Leadership Academy, a charter middle school in Dorchester, MA, reported being targeted by racist speech from MFA staff and visitors and racial profiling by security. In the weeks since, the MFA has conducted investigations into the events, banned the visitors who made racist comments, opened discourse between museum and Davis Academy leadership, and organized community roundtables to begin the healing process.
Toward a More Inclusive MFA details the MFA’s responses to the Davis Academy visit and updates regarding MFA efforts regarding inclusion in the institution at large. Such transformation takes time and needs certain elements to foster change among individuals and at the institutional level. The five elements needed for transformative climate change as identified by Eckel & Kezar (2003b) are senior administrative support, collaborative leadership, flexible vision, faculty/staff development, and visible action. How have MFA efforts aligned with these five elements?
1. Senior Administrative Support
MFA leadership has been involved in these efforts from the
beginning. Matthew Teitelbaum, director of the MFA, has been quoted often in
stories from news sites. Museum-issued statements have come jointly from the
chiefs of each department at the MFA. Makeeba McCreary, Chief of Learning and
Community Engagement at the MFA, reached out to Davis Academy leadership
herself to start the reparative process and has organized a series of
roundtables on inclusion and race among educational and non-profit leaders in
the Boston area.
2. Collaborative Leadership
As all information regarding this process is coming from MFA
leadership, it appears that all of these measures are mandated by MFA
leadership. Whether staff at different levels have had or will have input into
the process is unknown. However, MFA leadership has openly collaborated with
the community on this issue. They have been engaged with Davis Academy
leadership since the incident and have opened discourse with community members
regarding inclusion and racial equity.
3. Flexible Vision
Because museums serve the public at large, it behooves them to leave the specifics of “who for” and “how” open-ended. This way, museums can (theoretically) respond to trends with greater agility. The MFA does not have a clearly defined vision statement; instead, the mission is supplemented with statements in the MFA 2020 strategic plan and inclusion statements in Toward a More Inclusive MFA. In this time of action, MFA leadership should consider revisiting the mission. It was written in 1991 and, while flexible, it is old and places primary emphasis on caring for the collection. The idea is not to bring the focus so far away from collections, as Chet Orloff warns against in “Should Museums Change Our Mission and Become Agencies of Social Justice?” (Orloff, 2017); rather, it is to explicitly express that visitors are as valued as the objects within the museum’s walls.
4. Faculty/Staff Development
Among the first measures announced by the MFA were staff trainings
on conflict resolution and unconscious bias. Trainings were scheduled for June
and July and some have already been completed. Similar volunteer trainings are
being scheduled, but the timeline there is unknown. Information on follow-up
sessions is unavailable, but the MFA has also noted that they contracted
external consultants to “expedite and evolve” ongoing training in which all
staff is required to participate. (“Toward a More
Inclusive MFA,” 2019)
Before the Davis Academy visit, the MFA had already been working toward diversifying its staff through new recruitment methods, including adding paid teen internships and mentorship programs. Further steps toward enabling individuals from diverse backgrounds to earn a meaningful, sustainable living at the MFA include raising wages, adding full-time entry-level positions (and therefore benefits), and changing the requirements of and language in job descriptions. The Design Museum Foundation offers an excellent example of inclusive language in a job posting:
We know there are great candidates who may not fit into what we’ve described above, or who have skills we haven’t thought of. If that’s you, don’t hesitate to apply and tell us about yourself. We are committed to diversity and building an inclusive environment for people of all backgrounds and ages. We especially encourage members of traditionally underrepresented communities to apply, including women, people of color, LGBTQ people, and people with disabilities.
(“Marketing Manager – Foundation,” n.d.)
5. Visible Action
Towards a More Inclusive MFA is updated weekly with
notes on completed trainings, results from investigations, and responses to news
stories. People can also subscribe to the MFA email list to receive notice of
updates as they happen. Some change can already be seen and heard in the museum
more staff has been added to the galleries and school groups entrance. They
have also changed the greeting used for school groups to be more welcoming and
to avoid confusion with hurtful speech.
It goes without saying that the road toward healing and
toward a more inclusive MFA will be long and challenging. The efforts so far
are promising in terms of meeting the recommended elements for transformative
climate change, though there is always room for improvement.
What are your thoughts on the matter?
Continue reading